The Port of Rotterdam stakeholders will be able to participate and benefit from an untappable, multi-user quantum network for their critical communication systems. Several countries already experiment with quantum communication, but QuTech’s spin-off Q*Bird is the first to deploy a new type secure quantum network that can connect multiple users via a center hub in a cost-effective and scalable manner. This will ensure an untappable internet connection between many users, spread out throughout the harbour area.
The Port of Rotterdam represents a significant portion of the Dutch economy, handles almost 15 million shipping containers yearly and is therefore one of the largest ports in the world. Securing its communication systems will improve the safety of tens of thousands of sea ships yearly and for a significant part the economical traffic that comes after.
The safeguard of information transfer over the global internet is paramount for any large organization. Tampering with information channels has major financial implications and can be potentially life-threatening.

Economic impact
The port of Rotterdam is a crucial industrial and logistic hub that handles almost 15 million shipping containers yearly, and together with dry bulk cargo, wet bulk cargo (like oil), and breakbulk amounts to a total of almost 500 million tons of throughput. The total economic added value of the port represents 8.2% of the Dutch GDP (€ 63 billion), employing more than 500.000 people directly and indirectly.
Malignant tapping the communication systems between parties can lead to significant financial losses, disruption of critical business operation, or physical harm. A quantum communication infrastructure will insure an untappable connection and will improve the logistics chains of which Rotterdam is a part of, even more so a vital infrastructure on the European continent.
Special quantum key distribution technique developed by Q*Bird
Previously a team of scientists and engineers at QuTech—a collaboration between the Delft University of Technology and TNO—has demonstrated an alternative, untappable method for sending encrypted information. The technology has such commercial potential that they have decided to spin-off out of QuTech under the name of Q*Bird. “Our technology is based on a special implementation of quantum key distribution (QKD) that uses a central hub to connect users that want to exchange secure communications,” explains Q*Bird’s co-founder and director Remon Berrevoets. “That means that it is possible to implement a quantum network in a cost-effective way, scalable to many end-users, and using mostly off-the-shelf equipment.”
Co-founder and director Ingrid Romijn: “Our quantum secure communication system has already shown to be fruitful during a proof-of-concept at major Dutch telecom provider KPN with Cisco hardware and the deployed testbed at digital infrastructure provider Eurofiber with Juniper hardware. The port of Rotterdam as a launching partner displays the enormous potential of our technology.”
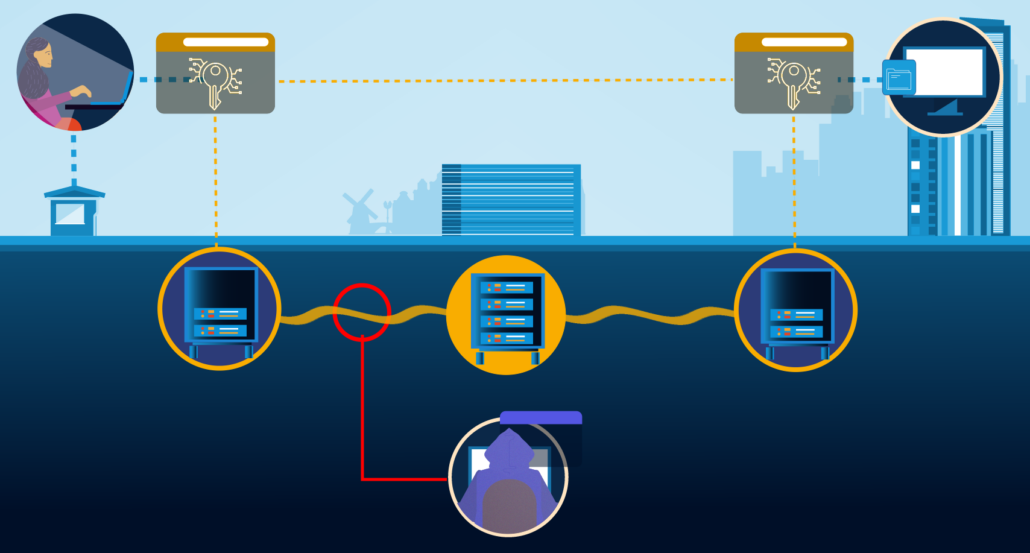
Schematic image of the quantum key distribution system. A central node (Charlie) connects users Alice (left) and Bob (right). If an eavesdropping hacker tries to steal the secret keys, the laws of quantum mechanics ensures the users are informed if the keys are compromised. Another set of keys will then be created to securely encrypt further messages. Image credit: Simplot for QuTech.
Practical implementation
As a first step in the test, the central hub for the distribution of quantum keys will be hosted at the Port of Rotterdam Authority. Using this new technology, data will be exchanged between a number of parties in the port in a closed environment. Participating in this test will be the Port of Rotterdam Authority, Portbase and a number of nautical service providers. The aim of the test is to further validate the technical capabilities of the system.
In the future, such a setup enables connecting all end-users with a secure, untappable connection. The first four end-users can be expanded later to many more. The users will share keys that are generated using quantum technology (and therefor inherently un-tappable) that they will use to encrypt messages using traditional technology. The strength of this type of setup is the ease by which it can be expanded to many more users, and the relative low cost of expansion. Upon completion, the parties concerned can be sure its communication line hasn’t been tampered with while connecting with.
Close collaborations
Delft-based Single Quantum is the first European company to commercialize superconducting nanowire single photon detectors (SNSPDs). With their 10 years of experience developing their product, they will provide a major component for the central hub of the quantum communication system. On the technical side, this project enables a close collaboration between Single Quantum and Q*bird: two dutch high-tech companies with complementary expertise and global ambitions. By joining forces in this project, they will have a powerful societal impact in the region.
InnovationQuarter helped think about and implement this project, for example, by co-producing the Birch report (Dutch). During its research phase several leads have emerged that helped shape this consortium. Jacqueline Schardijn, Senior Business Developer Digital Technology, InnovationQuarter adds: “Birch has indicated that we need to capitalise on opportunities in the region, by also working as governments and industry, towards a working communication infrastructure. As such, I have spoken to various parties who have a strong interest in a working communication infrastructure.”

Representatives of the many parties involved in this project: QuTech/Q*Bird, Port of Rotterdam, Single Quantum, InnovationQuarter, Portbase, pilotage, Cisco, Intel, Port Harbour Master, and Quantum Delta NL. Photo credit: Guus Schoonewille for QuTech.
Commercial and European implications
“It is one of QuTech’s goals to license technology or birth spin-offs whenever we have technology that is market-ready” says Kees Eijkel, QuTech director of business development. “Q*Bird perfectly shows how we as a research institute create impact: by solving academic challenges, recognizing the societal implications, and making the technology available to the world.”
Director of the Quantum Internet Alliance and QuTech group leader Stephanie Wehner adds: “Delft has a unique position in the development of the quantum internet. We want to build prototype networks and a framework for a European quantum internet. The work of Q*Bird is a great case of the commercial opportunity such networks have.”
Funding
Funding for this project has been provided for 2/3rds through the Quantum Delta NL SME programme and 1/3rd by the Port of Rotterdam.










